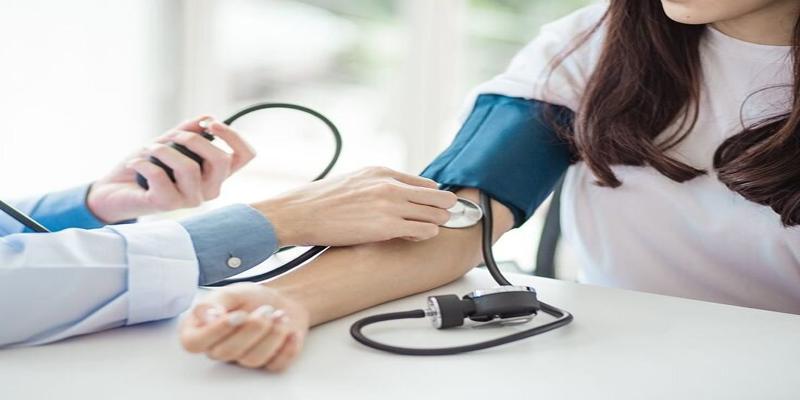
Ever wonder why your doctor checks your blood pressure in both arms? More than just a number, this deceptively simple practice can reveal much. In this comprehensive review, we discuss the implications, what such uneven blood pressure readings may indicate about your health, and steps you can take to help protect your cardiovascular well-being.
Understanding Blood Pressure Differences Between Arms
 What Causes Arm-to-Arm Variations?
What Causes Arm-to-Arm Variations?
Blood pressure variation between arms is common, a lot more than many think. Minor differences may be taken to be expected, but the greater ones may be warning signs of impending health problems. The following are some of the causes for these differences:
- Atherosclerosis: Deposition of plaque in arteries leads to narrowing arteries and hence reduced flow in one arm.
- Peripheral artery disease affects the flow of blood and may be one cause of this variation in pressure.
- Aortic dissection: A rare but serious condition where the inner layer of the aorta tears, altering blood flow.
- Subclavian steal syndrome: A disorder where blood flow is redirected from one arm to the brain, causing pressure differences.
Interpreting the Numbers
It's important to know what is considered a meaningful difference. More than a ten mmHg difference in systolic pressure (the top number) between arms is considered noteworthy. Here's what you need to know:
- A 10-15 mmHg difference merits further testing.
- Differences more significant than 15 mmHg may be associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
- Differences that exist consistently over time are more meaningful than isolated differences.
Significance of Bilateral Measurements
The blood pressure reading in both arms is an easy and fantastic way to detect possible cardiovascular risks. This practice can:
- Identify early signs of peripheral artery disease.
- Determine the risk of cardiovascular events in the future.
- Accurate diagnosis and treatment of hypertension
Causes for Difference between Arm Blood Pressure Readings
 Peripheral Artery Disease
Peripheral Artery Disease
The main reasons for the difference in blood pressure between the two arms include peripheral artery disease. It is a condition whereby arteries in the limbs narrow down or block. Most cases of narrowing or blockage are due to atherosclerosis. During atherosclerosis, plaque builds up in arteries and limits blood flow. This limited blood flow in the PAD may lower blood pressure readings in the affected arm. That may act as an early warning symptom for cardiovascular issues.
Subclavian Artery Stenosis
Other causes include subclavian artery stenosis, characterized by narrowing of the subclavian artery that supplies blood to the arm. This might eventually lead to lowered blood pressure in one arm. Subclavian artery stenosis is most often associated with atherosclerosis and may be indicative of a more general cardiovascular disease.
Aortic Dissection
An unusual yet profound difference in the blood pressure of both arms may indicate aortic dissection. This is a life-threatening condition wherein the inner layer of the aorta tears, allowing blood to pass between the layers of the aortic wall. Aortic dissection can lead to variation in blood flow to one arm, causing a vast blood pressure difference.
Other Contributing Factors
Various other reasons account for blood pressure variability between arms:
- Anatomical: People with minor anatomical issues or structural abnormalities in arteries on the right or the left may have very small differences in their blood pressure.
- Coarctation of the aorta: This is a congenital heart defect by birth where narrowing of the aorta has taken place, which would, in turn, decrease blood flow to one arm.
Takayasu's arteritis is an unusual inflammatory condition that could narrow the aorta and its branches, possibly causing blood pressure differences between arms.
Possible Health Consequences of Unequal Arm Blood Pressure
It may be more than interesting to find a significant difference in blood pressure between your arms; this may point to health issues that require attention. Understanding such possible implications is essential for general cardiovascular health and avoiding serious complications.
Risk for Cardiovascular Disease
A significant difference in the blood pressure readings between the arms usually warns of cardiovascular disease. Several studies suggest that a ten mmHg difference in systolic pressure between both arms may determine the possibility of developing peripheral artery disease, marked by poor limb circulation. This difference has also been linked to an increased risk of coronary artery disease and an overall higher risk of future cardiovascular events.
Subclavian Artery Stenosis
Unequal arm blood pressure can indicate subclavian artery stenosis, a condition in which the narrowing of the artery supplying blood to the arm leads to poor circulation and, thus, lower blood pressure in the concerned arm. When left without treatment, subclavian artery stenosis can cause arm pain and weakness, and severe cases might compromise the blood supply to the brain.
Aortic Dissection Warning
Significant but rare arm blood pressure differences may then be an early warning of aortic dissection, a life-threatening emergency wherein the inner wall layer of the aorta ruptures. This emergency requires immediate medical intervention to prevent serious complications or even death in a short period.
Diagnosis and Measurement of Arm Blood Pressure Difference
How Diagnosis is Made
The diagnosis of blood pressure variation between arms is approached in a structured manner by healthcare professionals. You will usually be subjected to several readings using a standard blood pressure cuff. Your doctor will take readings from both arms when you are seated comfortably. The catch here is that more than one reading is needed; this should be done multiple times and at different times to bring accuracy.
Advanced Measurement Techniques
Your healthcare provider might recommend ambulatory blood pressure monitoring for more precise results. This involves wearing a portable device that measures your blood pressure regularly throughout the day and night. This method can reveal patterns and fluctuations that might not be apparent during a single office visit.
Interpreting the Results
A difference in systolic blood pressure- the top number of ten mmHg or greater between arms- is generally considered significant. However, even less than this amount may be noted, especially if it is consistent over time. Your doctor will interpret these results regarding your overall health, risk factors, and medical history.
Follow-up and Further Testing
If a significant difference is noticed, your doctor may order additional tests to determine possible underlying causes. These may include Doppler ultrasound to study the blood flow through your arteries, CT angiography to examine your blood vessels closely, and blood tests to diagnose diabetes or high cholesterol.
Conclusion
Therefore, it is essential to understand the differences in blood pressure of both arms in light of your cardiovascular health. Where a slight difference may be inconsequential, a continued greater-than-10 mmHg difference between the two arms could presage underlying vascular problems. Knowing this as a potential warning sign and discussing it with your healthcare professional can be very advantageous in protecting your heart and circulatory system.